Last Update: September 24, 2024
A Fair Value Gap, or FVG, is one of the crucial elements in ICT trading concepts. Many profitable ICT traders use it as their primary entry point. Even my personal trading is based on the Fair Value Gap strategy, both for entering and exiting trades. Therefore, understanding what an FVG is and how you can trade it can be a key factor for your trading success.
In this article, I’ll delve into the details of what a Fair Value Gap is in trading and how to find the right ones. Being one of the most important ICT concepts, I’ll try my best to explain it in the simplest way and provide some examples on charts so you can better understand this essential pattern.
For more examples, check out my ICT trades journal article, which I update with the real trades I take based on the ICT strategy.
Key Takeaways
- Fair Value Gaps (FVGs) represent imbalances in the market where a candle’s body is not filled by the previous or next candle.
- There are two types of FVGs: Bullish FVGs act as support levels, while Bearish FVGs serve as resistance levels.
- FVGs can be used as entry and exit points for trades, as they attract price movements due to liquidity voids.
- Traders should use FVGs in premium and discount zones, wait for price reactions, and trade only during ICT Killzones for better success.
- It’s advised to avoid large FVGs and to prioritize those formed after liquidity hunts for higher accuracy.

What Is FVG in Trading?
So, what is Fair Value Gap in trading? Well, In order to grasp the idea behind them, you should first understand what an imbalance is. An imbalance is a situation in the market where there is a significant difference between buy and sell orders. Imbalances are liquidity voids which the price is likely to revisit and rebound from.
A Fair Value Gap is essentially the same as an imbalance. To identify it, you should look at areas on the chart where a candle’s body is not filled by the previous or the next candle. Therefore, an FVG is a three-candle chart pattern.
There are two types of Fair Value Gaps:
- Bullish FVG: A bullish Fair Value Gap forms when the middle (imbalance) candle is bullish.
- Bearish FVG: A bearish Fair Value Gap forms when the middle (imbalance) candle is bearish.
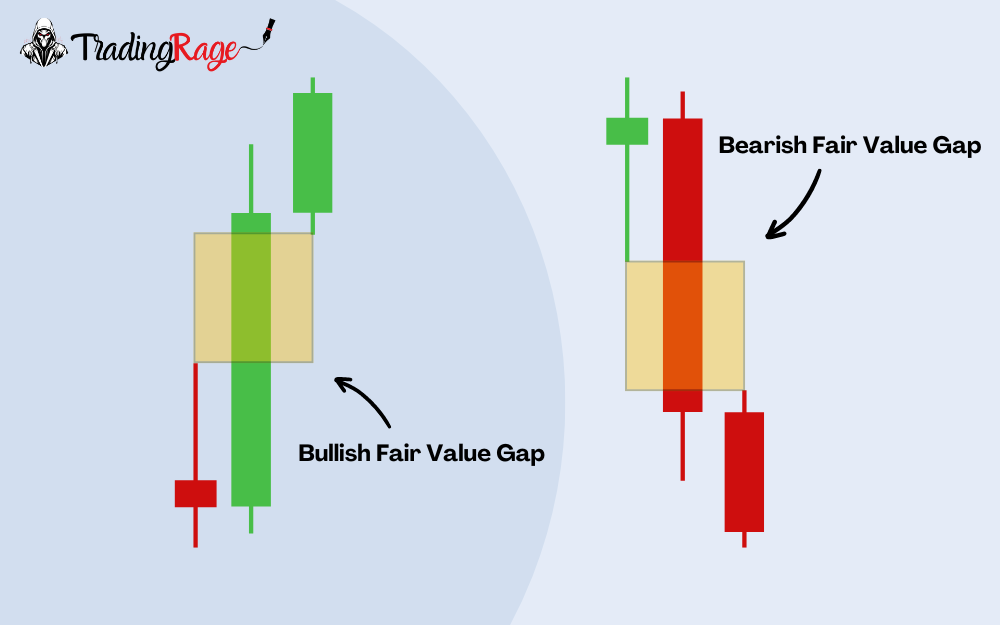
How to Identify Fair Value Gaps?
The first step for executing the Fair Value Gap strategy is finding the right one. In order to identify Fair Value Gaps, you should first determine the trend. In bullish trends, look for a candle that is not engulfed by its prior or next candle. This means that a part (or all) of this candle’s body should not be traded into by the last or next candle’s wicks. This part of the body is your bullish FVG. Note that the first and third candles in a bullish FVG trading pattern can be bearish. Only the FVG candle should be bullish.
Similarly, to identify a bearish Fair Value Gap, look at a bearish trend. Search for a bearish candle that is not engulfed by the candle before or after. The area of the middle candle’s body, which is not traded into by the two candles nearby, will be the bearish FVG. Again, the first and third candles in a bearish FVG trading pattern can be bullish.
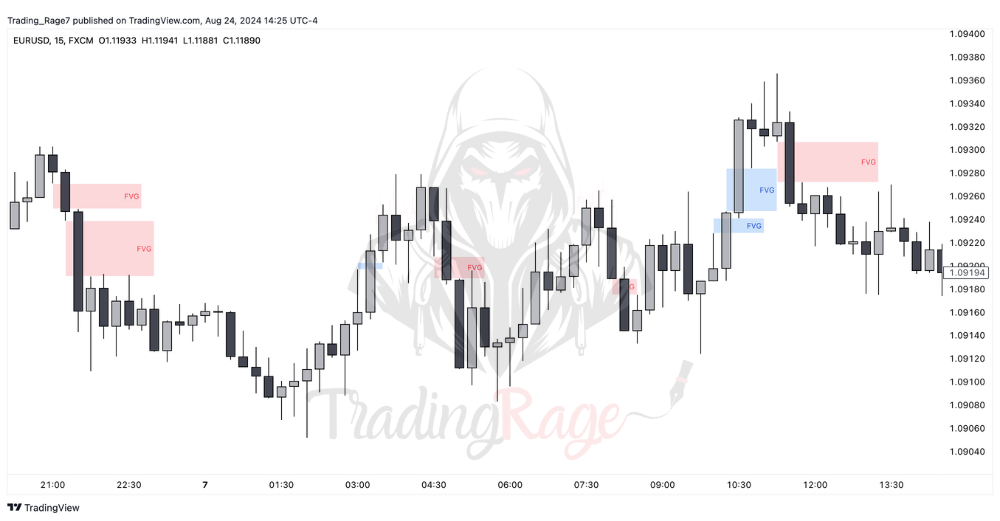
Take a look at the image below, where I’ve specified several bullish and bearish FVGs:
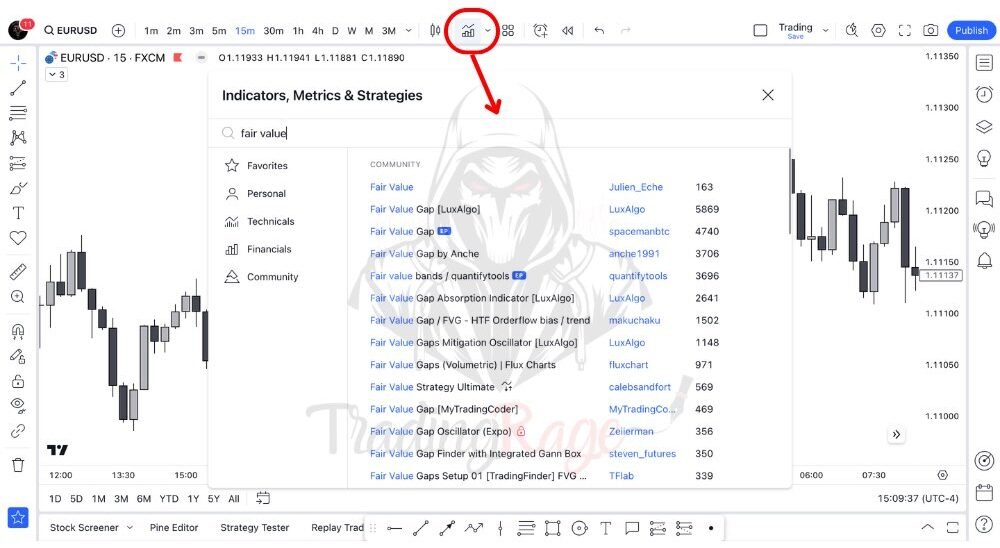
Using Fair Value Gap Indicators on TradingView
Finding fair value gaps is not challenging at all, and it gets even easier as you practice more. However, you might prefer a more automated way of identifying them. Well, you’re in luck, as there are several accurate FVG indicators available on TradingView. You can easily search the term “Fair Value Gap” in the TradingView indicators search bar and test which one you like the most.
How To Trade Fair Value Gaps?
As I’ve already mentioned, ICT FVGs are imbalances. They are liquidity voids that can attract the price and also work as support and resistance levels. This is why I use them both for entry and take profit levels.
Bullish Fair Value Gaps can be used as support levels. So, you can utilize them as entry points for your longs (buys).
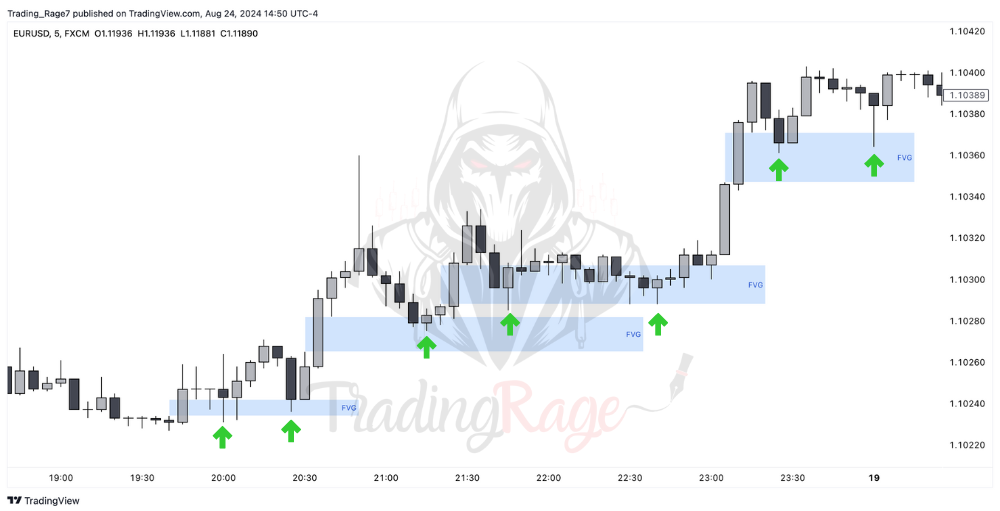
On the other hand, bearish Fair Value Gaps act as resistance levels and can be used as entry zones for shorts (sells).
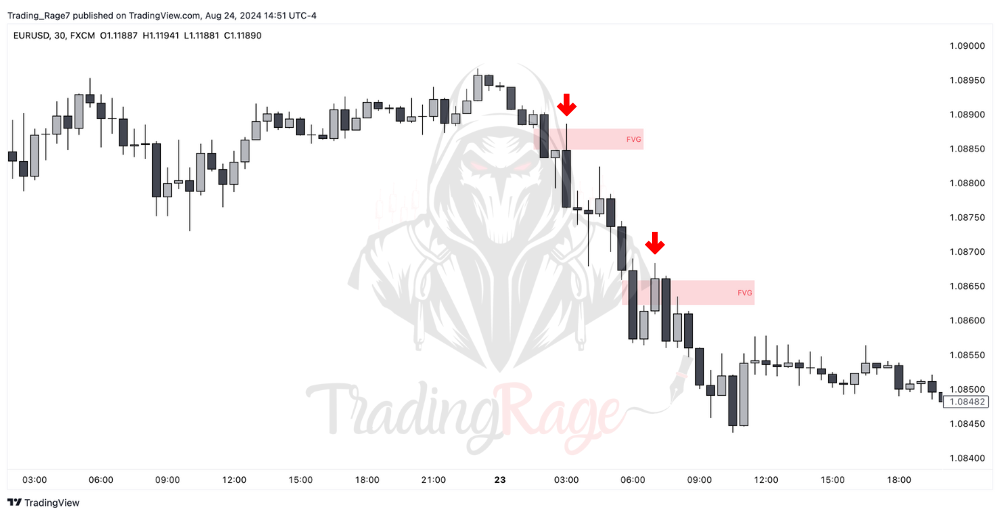
Additionally, you can use a bullish FVG as a target for your short position. Similarly, bearish fair value gaps can be used as targets for long positions. The reason is that these imbalances are essentially considered liquidity voids, and in ICT concepts, we expect them to draw the price.
Pro Tips on Trading FVGs
Finding Fair Value Gaps is arguably one of the simplest things you can do as an ICT trader. However, identifying the right one and knowing how to trade it is what separates profitable traders from others.
Here are some tips and tricks I’ve learned during my ICT trading journey:
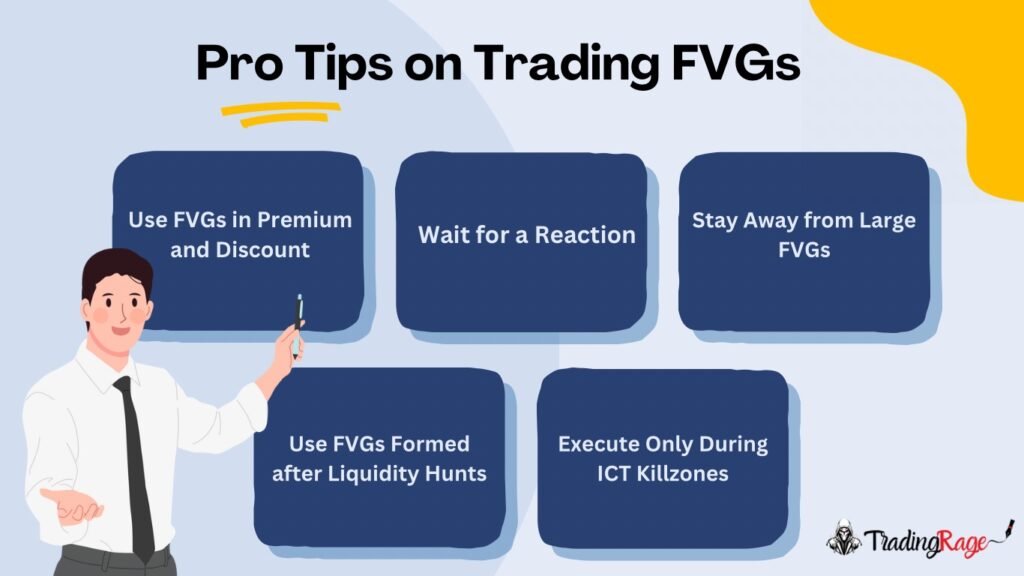
- Use FVGs in Premium and Discount: Not every FVG can act as a support and resistance level. So, use the ones in discount (if you’re buying) or premium (if you’re selling), as these are most likely to be the best Fair Value Gap entry points. You can also rely on the ICT Power of 3 framework to locate the right FVG.
- Wait for a Reaction: I always wait for the price to react to my target Fair Value Gap before entering. While others might prefer to enter as soon as possible for better reward/risk ratios or because of FOMO, I prefer more winning probability.
- Stay Away from Large FVGs: I never trade large Fair Value Gaps trading patterns, especially when the price returns to the after a long while. In my experience, these mostly fail as the price quickly moves through them.
- Use FVGs Formed after Liquidity Hunts: As with almost all ICT entry models, wait for the price to sweep liquidity before entering a Fair Value Gap. FVG trading patterns formed after liquidity hunts are usually the strongest.
- Execute Only During ICT Killzones: I never trade outside the ICT killzone times. This is because I believe these are the times when the market is volatile enough for you to catch significant moves. So, no matter how many imbalances I see, if we are not in the ICT Killzone times, I’m not entering a trade.
Read More: What Is an Order Block?
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve explained what an FVG is and how you can use the Fair Value Gap strategy. FVGs are one of the essential elements in ICT trading concepts, and many ICT traders use them as their primary trading strategy. Even if you use a different trading strategy, you can implement them as an additional tool. Therefore, understanding them can boost your trading performance.
If you have any questions, feel free to ask them in the comment section or send an email via the Contact page.
Disclaimer: All the information in this post is for educational purposes only and should not be considered investment advice. Trading in the financial markets is a high-risk endeavor. So, make sure to protect your capital at all times.




